The EAN (European Article Numbering) is an 8 or 13 digit barcode identifying a unique product, which is used in trade and industry.
History of the EAN code
It was in the United States, after the Second World War, that the idea of a barcode appeared. Following the end of the war, the number of self-service stores exploded, and the problems of labeling, inventory management and checkout were felt.

Two American students, Norman Joseph Woodland and Bernard Silver found a solution to automate and easily identify a product : the barcode was born. At the time, it was shaped like a circle so that it could be scanned from all sides.
Between the first patent in 1949 and its first use in 1974, the technology was the biggest obstacle to the future EAN, and an agreement also had to be found between distributors and manufacturers.

It’s on a packet of chewing gum in an Ohio supermarket that the ancestor of the EAN, the UPC (Universal Product, 12-digit code and still used in the USA) is making its big arrival.
The idea gained momentum in Europe and in 1977, the EAN was born, consisting of 13 digits. Very quickly, 150 countries will use this barcode. Thanks to the famous hand shower, barcode reading becomes possible and makes it possible to recognize a product in store instantly.
The first French product with the EAN was a galette package, in 1980, and in 1982, Carrefour and Casino fitted their stores with barcode readers. It was not until the end of the 90s that all stores were equipped with it.
The revolution brought by barcodes is enormous : reduction in checkout time, 40% reduction in costs, more security in transactions, inventory management is optimized. Today, it is more than 8 billion beeps per day in the world. The strength of this system lies in the fact that it brings everyone together : distributors, suppliers … It is the non-profit organization GS1 (Global Standard One) that assigns the EAN codes. GS1 is constantly evolving the EAN, to ensure today 100% product traceability.
“The bar code is ultimately the first standard, the one everyone uses today in the world of commerce.”
On the web, the EAN code also makes it possible to identify a product, and thus to constitute and manage its product catalog, in particular on marketplaces.
What is the EAN for?
The EAN code makes it possible to identify a product (or packaging), making it possible to follow its traceability and to know its characteristics and its purpose is to
“Concentrate a maximum of information on a minimum of space” according to Pierre Georget
The EAN is present in most countries of the world, and has been defined as a European standard model since 1997. It is universally used to identify the sales units of large retailers.
It is present on all types of consumer goods : clothing, books, food, medicine, mail.
The advantages of the EAN code
EAN codes have 3 advantages:
- Automatic product recognition : it makes it possible to identify its product, its stock, its location, its price and therefore to be able to follow its evolution.
- Traceability : the EAN allows to know the life cycle of a product : from its origin to its end consumer
- Time saving : inventory management is simplified and optimized thanks to the EAN.
EAN codes on marketplaces
On marketplaces, the EAN is used to identify a unique product. It is thanks to him that we can reference thousands of products, whether on Amazon, Fnac, Rakuten …
Marketplaces have adopted the EAN to facilitate the referencing of products on their site. This means that all the offers on the marketplaces are made from the EAN-SKU pair (Stock Keeping Unit, the seller’s internal reference). This couple is unique and allows an efficient management of an online inventory, especially in the management of an e-commerce flow.
GS1 is the organization recommended by all marketplaces to obtain its EAN codes, thanks to the GTIN system (Global Trade Item Number). GS1 distributes and regulates barcodes internationally. In particular, they monitor that a company does not have a duplicate EAN code, for example.
If you use another site to provide you with these codes, you cannot be sure that you are the only ones using them. This poses a major drawback : If you have an EAN code for your product that does not come from a trusted source, your product could end up attached to a different product, which has the same EAN as you. According to the organization, 10% of EAN codes are incorrect on the web.
In addition to making it possible to identify a product, the EAN code has several advantages :
- It helps move up in Google search results. According to the latter, the click-through rate is higher on listings with an EAN, and we record 20 to 40% of additional sales.
- Having a good EAN code allows you to take advantage of information from product sheets already created, but also to retrieve customer evaluations linked to this product sheet. Remember that, for Amazon for example, a good product sheet has a minimum of 15 customer reviews and an average of 3.5 / 5.
Structure of an EAN code
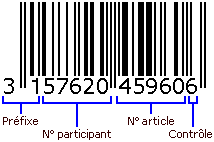
The most widely used EAN code is the EAN-13 code. As its name suggests, it is composed of 13 digits, structured in three parts :
- The company prefix : the first three digits represent the country of origin of the product (France : 300 to 379)
- The article number :
- the next five digits correspond to the manufacturer’s code (from 0 to 99 999)
- From 8 to 12 th digit, these are the numbers corresponding to the manufacturer’s product. So there are 99 999 possibilities for each manufacturer. These figures are ” free That is, each manufacturer can choose the numbers used.
- The control key : the 13 th and last digit is a check digit : it is calculated according to the first 12 digits of the EAN. This key is used to validate the barcode.
This code is symbolized by a sequence of white and black bars, thus becoming a bar code.
“This combination theoretically makes it possible to allocate a trillion codes” affirms Pierre Georget, former executive chairman of GS1 France.
The different types of bar codes
There are two kinds of barcode : linear (and stacked linear) barcodes, as well as two-dimensional barcodes.
The EAN is part of the first category. There are different EANs : EAN-8, EAN-13 and EAN-128. The EAN-8 code is used on small products and the EAN-13 on the rest of the products. The EAN-128 is not a barcode per se : it allows distributors and producers to exchange data. All of these EANs are GTIN codes. These codes may be different depending on the country and the type sold :
- UPC : 12 digits for the USA
- EAN : 13 figures for Europe
- JAN (Japanese Article Number) : 8 to 13 digits for Japan
- ISBN (International Standard Book Number) : 10 or 13 digits for books. This code is still used a lot on Amazon.
Composed of white and black bars, these codes are called linear because they can be read in the horizontal direction.
There are also stacked linear barcodes : they group together several bar codes, located on top of each other and are read vertically.

The best-known example of a two-dimensional barcode is the QR Code. Unlike the linear barcode, it can be read horizontally and vertically. They also make it possible to contain more information than a conventional barcode. These new codes are used mainly in advertising and distribution.
After having revolutionized the world of mass distribution, the EAN code has become an essential element on marketplaces. By providing precision and reliability, the EAN and its 13 digits make it possible to find oneself in the large catalog of web marketplaces.
